In this page
Working with GitLab Self-Managed commit policies
Installing GitLab Self-Managed hooks
Installing GitLab Self-Managed hooks for remote verification
Dedicated GitLab extension
Installing GitLab Self-Managed hooks for local verification
GitLab Self-Managed commits
Overview
This page is about implementing Better Commit Policy specifically in Git repositories managed by the GitLab Self-Managed application. If you use Git, but you don't use GitLab Self-Managed, see the general Git guide instead of this page.
Working with GitLab Self-Managed commit policies
GitLab Self-Managed builds on the top of the Git version control system, extending that with repository-, user- and permission management capabilities. As it is primarily a high-level management layer above Git, everything written in the general Git guide applies to the Git repositories managed by GitLab Self-Managed, too.
In the Better Commit Policy app's context, the only major difference between using Git alone and Git with GitLab Self-Managed is how you install the commit hooks to the central Git repository. (Installing hooks to the local Git repositories is the same for those two cases.)
Installing GitLab Self-Managed hooks
Installing GitLab Self-Managed hooks for remote verification
First, read the GitLab custom hooks page to learn how to install custom hook scripts to GitLab Self-Managed hosted Git repositories in general.
To install the hook script for Better Commit Policy, launch the Hook Script Wizard, select "Git" as VCS, select "in the central repository (remote)", and follow the steps until 1: Unpack the ZIP file to the location where Git expects it. At this step ignore the wizard's instructions, because GitLab is using a slightly different directory structure.
Instead, follow the instructions below:
-
Locate your Git repository in the server filesystem based on the storage behavior of your GitLab version:
- GitLab versions prior to 10.0: Legacy Storage
- Modern GitLab versions: Hashed Storage
- Extract the hook script package to a directory named custom_hooks inside your Git repository. If custom_hooks does not exist yet, create it.
-
Change the owner of the custom_hooks directory and all the files in it to git:git:
chown -R git:git /var/opt/gitlab/git-data/repositories/your_repository_dir/custom_hooks
-
Open jcp_git_common.py in a plain text editor, and...
-
Modify the method called is_existing_commit() to this:
def is_existing_commit(commit="HEAD"): import os if ("GIT_ALTERNATE_OBJECT_DIRECTORIES" in os.environ): # Disable the quarantine environment while checking the existence of the hash (pushed commits are by-definition existing in quarantine) original_git_object_directory = os.environ["GIT_OBJECT_DIRECTORY"] os.environ["GIT_OBJECT_DIRECTORY"] = os.environ["GIT_ALTERNATE_OBJECT_DIRECTORIES"] (results, code) = git("cat-file -e %s" % commit, pipe_errors=True) os.environ["GIT_OBJECT_DIRECTORY"] = original_git_object_directory return code == 0 else: jcp_common.logger.verbose("*** WARNING ***: Could not calculate 'isExisting' flag for commit %s, " "falling back to False. Check if you are using Git version 2.11 or newer!" % commit) return False -
Modify the method called started_manually() to this:
def started_manually(): is_gitlab = "gitlab" in sys.argv[0] and "/custom_hooks/" in sys.argv[0] return not sys.argv[0].startswith("hooks") and not is_gitlab and not sys.argv[0].startswith(".git")
-
Modify the method called is_existing_commit() to this:
-
In order to show rejection messages properly in the GitLab web-based file editor, there is one more change to make.
Open jcp_common.py in a plain text editor and modify the method called print_stderr(*s) to this:
output_started = False def print_stderr(*s): global output_started utf8_supported = not hook_platform.windows() or hook_platform.git() if utf8_supported: encoding = "utf-8" else: encoding = hook_platform.windows_encoding() for part in s: if not output_started: part = "GL-HOOK-ERR: " + part output_started = True part = part.replace("\n","\nGL-HOOK-ERR: ") if hook_platform.python3(): # to print utf-8 correctly, use raw interface for stderr if isinstance(part, str): # raw interface might need manual encoding part = part.encode(encoding, errors="ignore") sys.stderr.buffer.write(part) else: if isinstance(part, unicode): part = part.encode(encoding, errors="ignore") print(part, file=sys.stderr, end="")
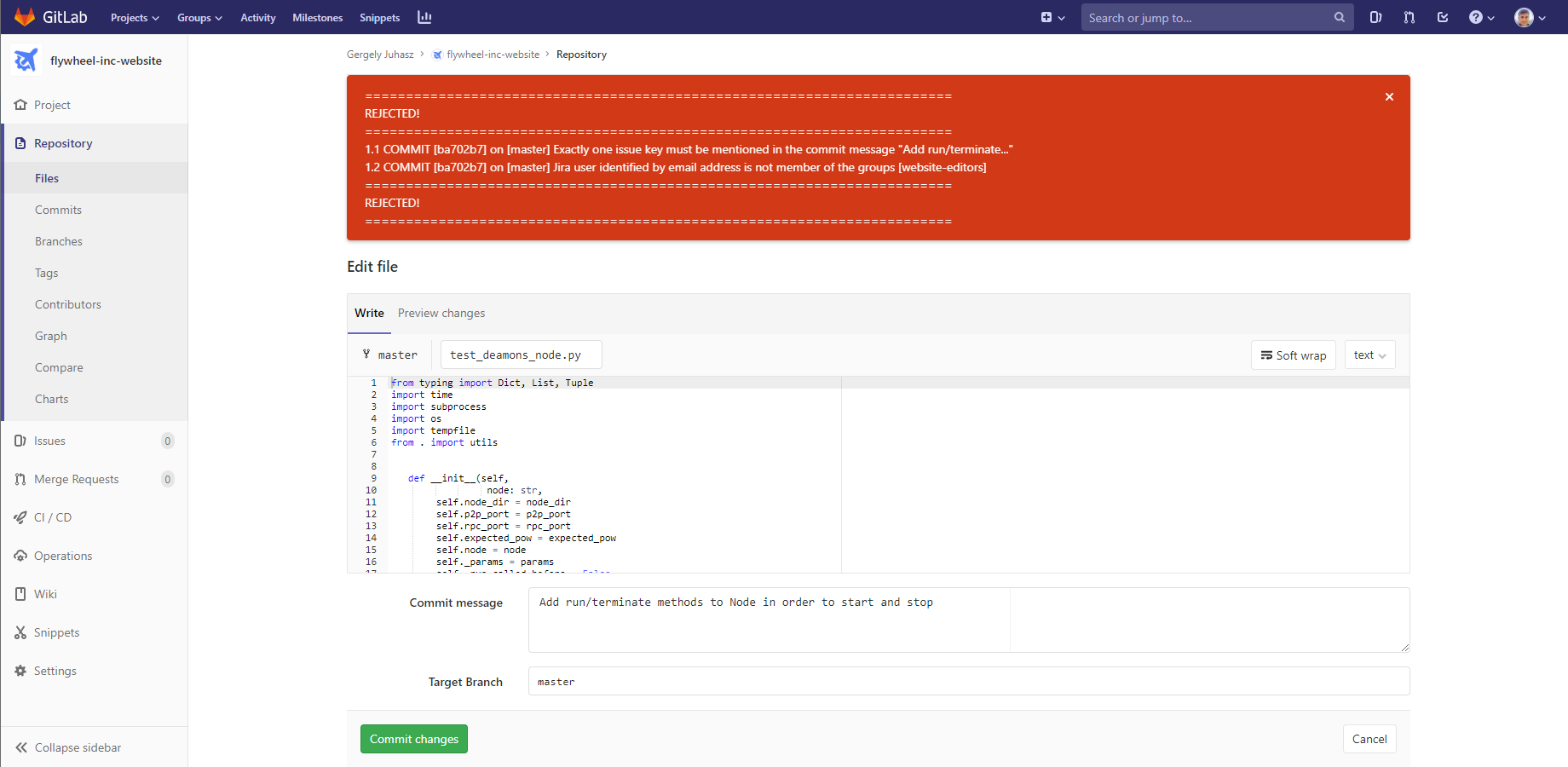
After this, you can continue executing the steps suggested by the wizard from 2: Set permissions and run a diagnostic test.
When completed, commit policies will be verified both when pushing commits to GitLab Self-Managed and when using the web-based file editor:
Dedicated GitLab extension
Although this solution works perfectly, it could be more convenient. We plan to make the installation process easier by developing a custom GitLab extension.
If you are interested in that, please vote for the feature request by clicking the "thumbs-up" icon. This is very important to get your vote, as we go through the most requested feature requests when planning an upcoming app version.
Also, add a comment with your use case and click "Follow" to be notified when there are updates on that story.
Installing GitLab Self-Managed hooks for local verification
Installing the local hook to a local Git repository which was cloned from a GitLab Self-Managed managed central repository is the same as installing that to any other local Git repository.
See the installing Git hooks for local verification section for detailed instructions.
GitLab Self-Managed commits
In your daily developer workflow, when creating commits and pushing those to GitLab Self-Managed, you can use your Git client exactly the same way as you would with Git alone.
See the Git commits section for detailed instructions.
Questions?
Ask us any time.